The use of chemicals to prevent and eliminate termites is widely used. But the impact on health and environment cannot be avoided.
Research & Innovation for Sustainability Center (RISC) therefore studies and recommends safe and healthy termite prevention methods. The use of chemicals and natural extracts may not solve the problem at the root cause. In addition, preventing or solving problems by eliminating other organisms that are important to the holistic ecosystem. Still does not really answer the question of sustainability. Creating good health must be done for all living things. By choosing a termite protection model that does not cause toxic substances for termites, humans, pets and the surrounding environment, but first, let’s get to know the nature and types of termites as follows.
Let’s get to know termites.
Termite (Termite) is a type of insect in the order (Order) Blattoidea and sub-order (Infraorder) Isoptera, divided into 7 families (Families), with a total of about 3,106 species. In Thailand, more than 310 species of termites are found and about 10 species are found. It is a wood-destroying termite (Jarunee Wongkaluang, 2018)

function of termites
The termite population is divided into 3 castes, namely:
- reproductive caste (Reproductives) , including the king (King) and queen or queen (Queen) serves to breed and lay eggs and moths (Alates) are both male and female. Do the matching task and find the right location to build a new nest.
- Workers caste or termites (Workers) have no eyes, no sex, use tentacles as organs for sensory and palpation. Serves for food for the termite population for the whole nest, builds nests, repairs nests, takes care of eggs, and some plants cultivate mushrooms and fungi.
- The Soldiers caste fights and prevents enemies from attacking the eggs and termite populations inside the nest.
food
Termites’ food is cellulose from plant fiber. Termites’ food sources include dry wood, moist wood, soil, humus, leaves, plant debris deposited on the ground and underground, lichens, moss, and other materials. containing cellulose as a constituent In the gastrointestinal tract of termites, there are protozoa or microorganisms, which help digest cellulose food as energy. Some termites can cultivate a fungus garden inside the nest for food (Fungus Growing Termite), for example, termites of the genus Macrotermes.
residence
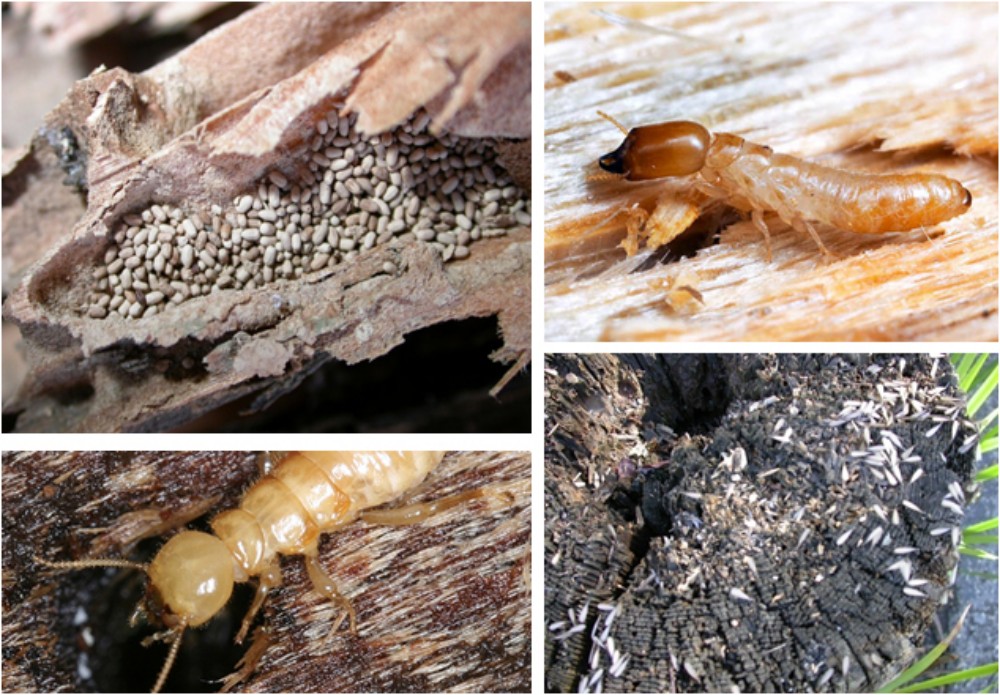

1. Wood Termites include dry wood termites (Drywood Termites), damp wood termites (Dampwood Termites).

2. Land termites (Land Termites) including subterranean termites (Subterranean Termites) termites in the mound (Mound-building Termites) and Carton Nest Termites
types of termites
The important types of termites in Thailand are:
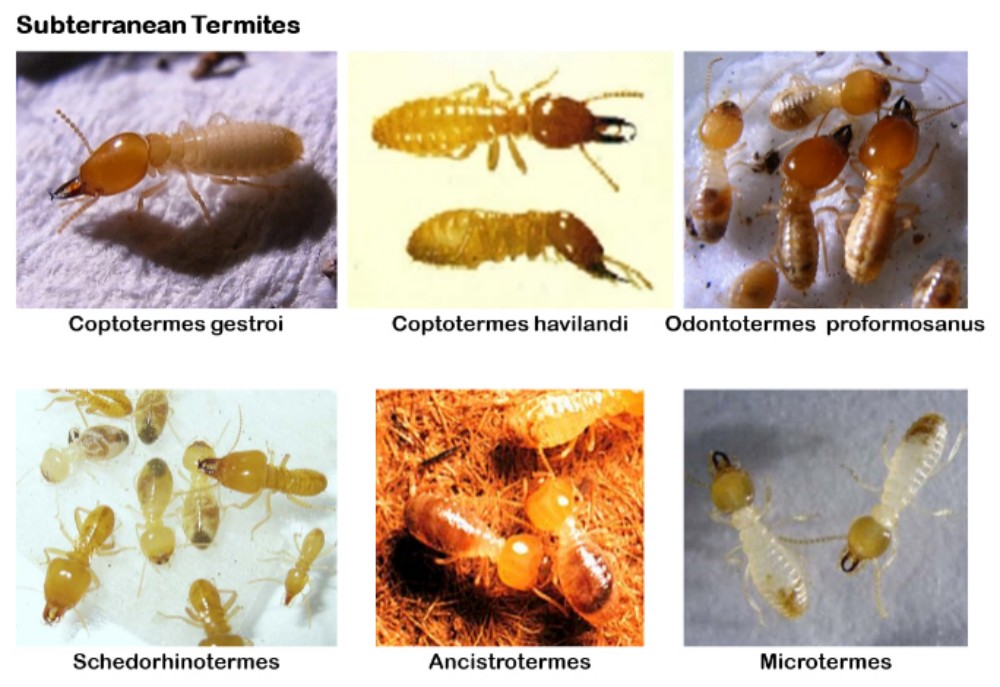


- The main subterranean termites are Coptotermes gestroi and Coptotermes havilandi . Coptotermes gestroi underground termites are classified as economically important.mHighest income in the country, 90% of the buildings destroyed are caused by the infestation of this type of termite. And more than 90 percent found damage to buildings in urban areas . and termites in the genus Schedorhinotermes, Ancistrotermes, and Microtermes may be found to damage utilization. Outside of buildings or houses in rural areas
- Dry wood termites, most importantly Cryptotermes thailandis , have been found to cause severe damage to buildings on the coast. especially in the southern area and the eastern part of the country
- Small nest-forming termites , mainly Microcerotermes crassus and Nasutittermes sp., have been found to damage wood for outdoor use or in rural dwellings.
- Medium- to large-sized nesting termites, notably Globitermes sulphureus, Macrotermes gilvus and Odontotermes longignathus , are often found to damage outdoor and rural timber.
So how are termites important to the ecosystem?
Termites are very important insects in forest ecosystems. The main benefits of termites include:
- Helps break down organic matter to become humus make the soil fertile As a result, trees, plants and forests grow well. which is the origin of the food chain in the ecosystem
- It is a food source for small animals, poultry, insects and reptiles. Because termites are rich in protein. which will become food for the larger animals in the food chain
- a source of food production Some types of termites can be cultivated for fungi. which is expensive can be a source of additional income for farmers
4 Principles and methods of termite control
Even termites are important to the ecosystem. But it affects the living. and considerable economic damage Therefore, it must be controlled and managed (Termite Management) with principles and methods for controlling termite populations according to the severity, efficiency and level of environmental toxicity as follows:
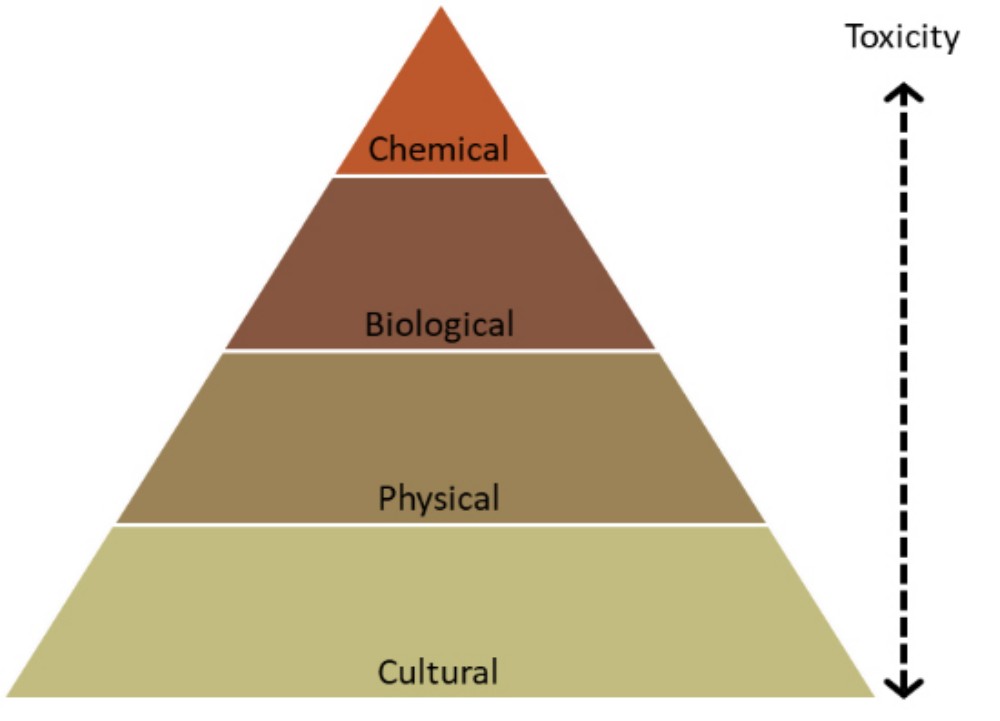
(Categorized by Pest Management and Control
, Source: https://www.ukenvironmentservices.co.uk/integrated-pest-management
- Cultural control is to improve the environment such as cleaning the construction area. Soil Inspection and Conditioning or reducing the use of building materials that are food for termites To reduce the factors that attract termites to nest. The advantage is that it does not cause toxic residues in the environment. Does not harm termites and other living things But there are limitations in the effectiveness of termite control.
- Physical control (Physical Control) is to control the territory of termites. by creating obstacles Either by mechanical or non-mechanical use such as water, oil, gravel, pebbles, the use of sealants along building joints and openings such as plastic sheets, metal sheets, metal grilles, the use of sound waves or the use of heat to remove Termites leave the territory and the use of traps (which can be released later), etc. The advantage is that it does not cause toxic residues in the environment. There are both harmful and non-harmful forms of termites. And most of them do not harm other living things. But there are limitations in the effectiveness of termite control. And some forms may interfere with the lives of termites and other organisms.
- Biological control is the control of termite populations with natural enemies such as the use of predators along the food chain in the ecosystem such as bats, musk, ferrets, chickens, birds (hawks, pigeons, sparrows), insects (ants, ladybugs, flies). Reptiles (lizards, geckos, frogs, snakes), etc., including the use of parasites, microorganisms, nematodes and fungi to eliminate termites. The advantage is that it does not cause toxic residues in the environment. But there are limitations in the effectiveness of termite control. And it is harmful to termites, both eliminating or altering the physical and reproductive systems of termites.
- Chemical Control (Chemical Control) is the use of chemicals or synthetic substances from nature injected. or placing bait to kill, disrupting the development of the life cycle. or to inhibit natural propagation which is a method of abuse should be chosen as the last resort The negative effects on the environment and other species should also be considered. The advantage is that the termite control efficiency is higher than that of the non-chemical form. But there is a limitation in terms of service life. must be carried out on a regular basis Harmful to termites and may also be harmful to other organisms. and has the potential to cause toxic residues in the environment
From the analysis of advantages and disadvantages of each principle of termite control methods When considering the sustainability of the ecosystem, it can be seen that The proper method is a combination. both karmic control methods physical control and biological control which is a non-toxic form of termite protection by limiting and avoiding chemical control methods For the good health of all living things, including termites, humans, pets and the surrounding environment
Examples of termite protection without creating toxins
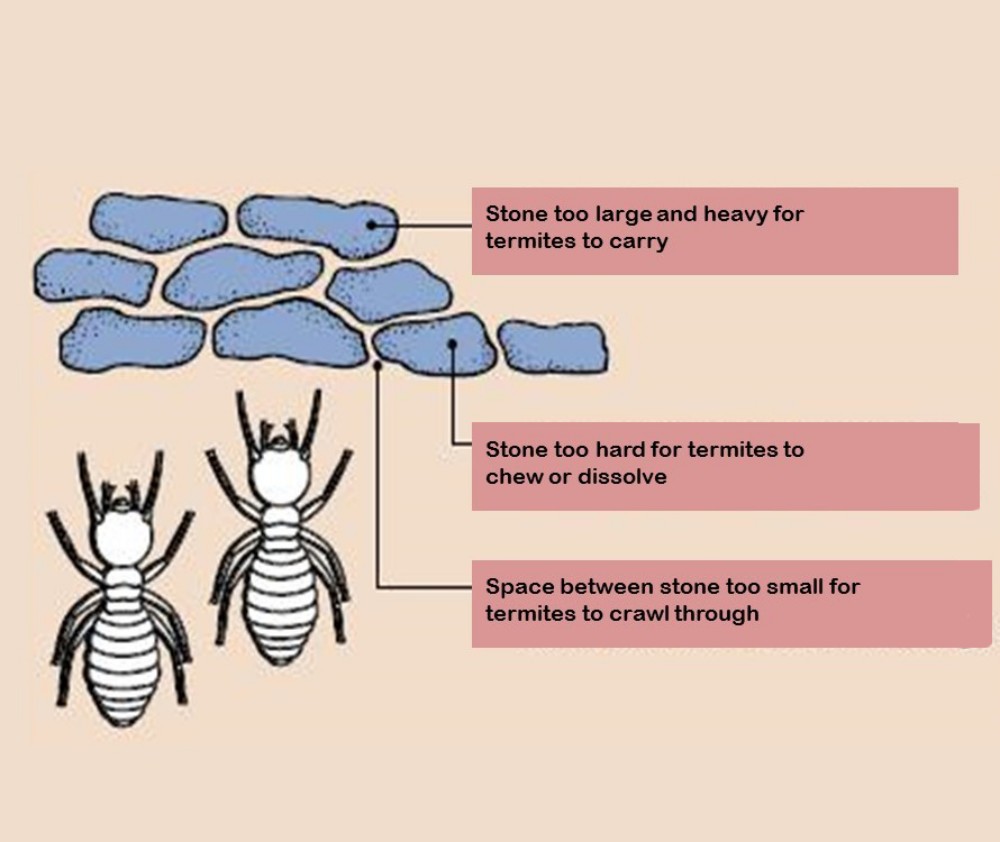
Source: http://granitgard.com.au/system-description
1. Foundation under the building with gravel or crushed stone (Graded Granite, Crushed Stone, Basaltic Rock) to prevent termites from underground. However, the subsidence of the soil layer and the groundwater level must be considered. This will create a gap between the rocks.
2. Foundation under the building floor or soil conditioning with salt, brine or salt compounds. to prevent termites from underground Structural erosion and soil quality must be considered for planting trees.

. Source: https://emedia.rmit.edu.au.
3. Construction of building bases in contact with the ground with stone or concrete. to prevent termites from underground However, construction techniques at the structural joints and crack solutions must be considered.
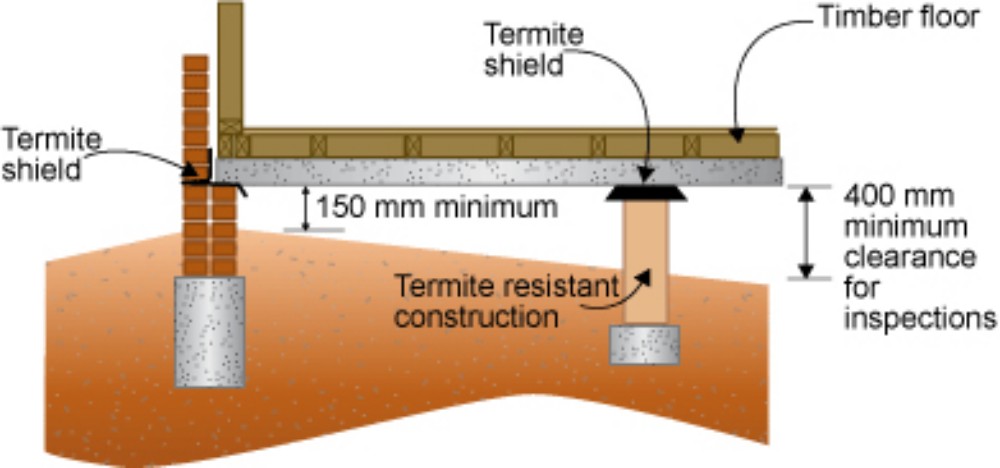
. Source: https://emedia.rmit.edu.au .
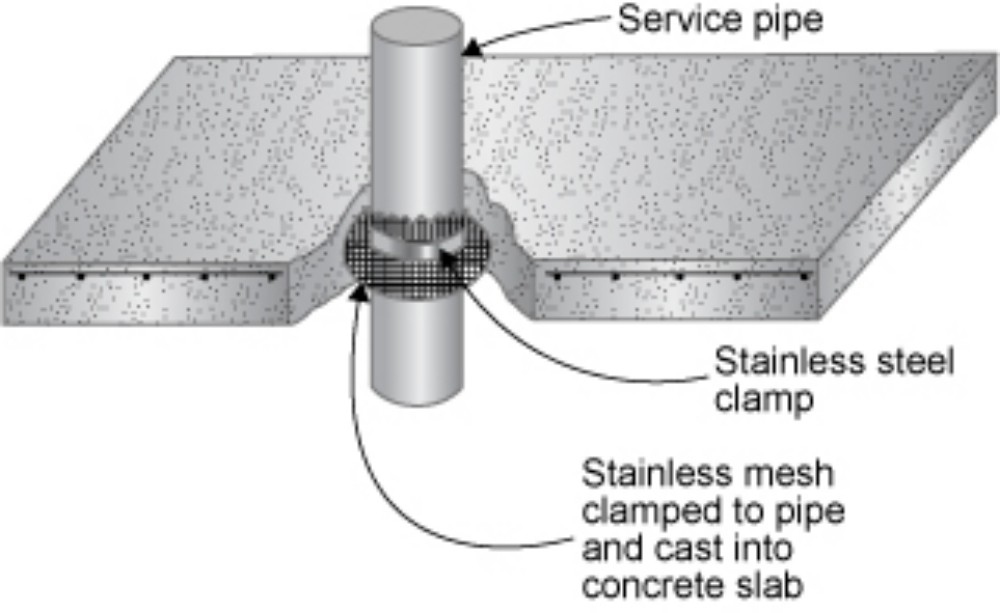
. Source: https://emedia.rmit.edu.au .
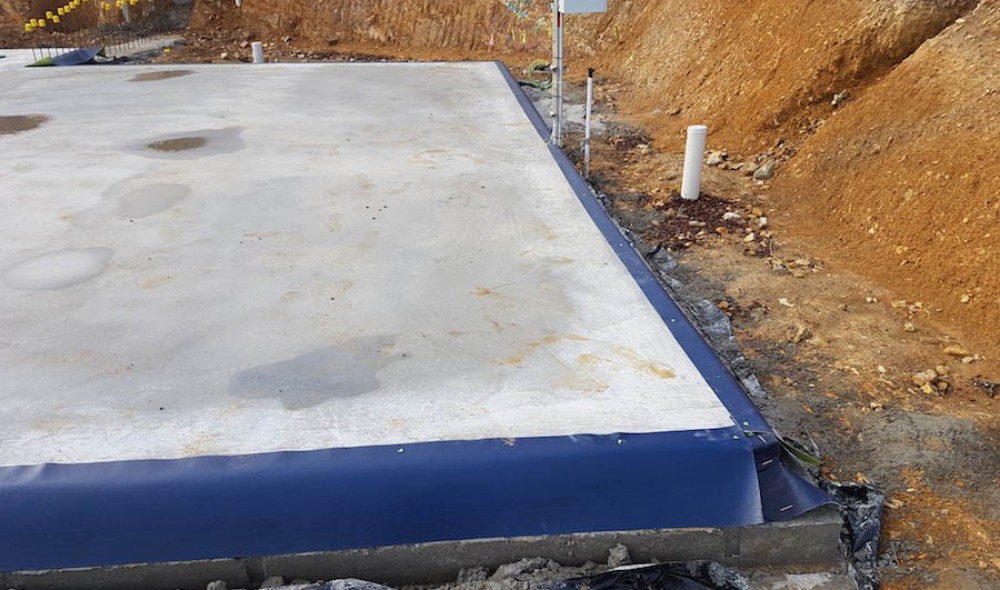

. Source: http://www.termitespecialist.com.au.
4. Cladding the joints of the underground structure and the edge of the building base with sheet metal, metal grating or plastic sheeting. to prevent termites from underground However, the quality control of skilled technicians, installers and contractors must be considered. to prevent system damage

Source: Center for the Study of Ancient Arts in Southeast Asia, Faculty of Archaeology. Database of Important Ancient Sites in the Northeastern Region, 2013.
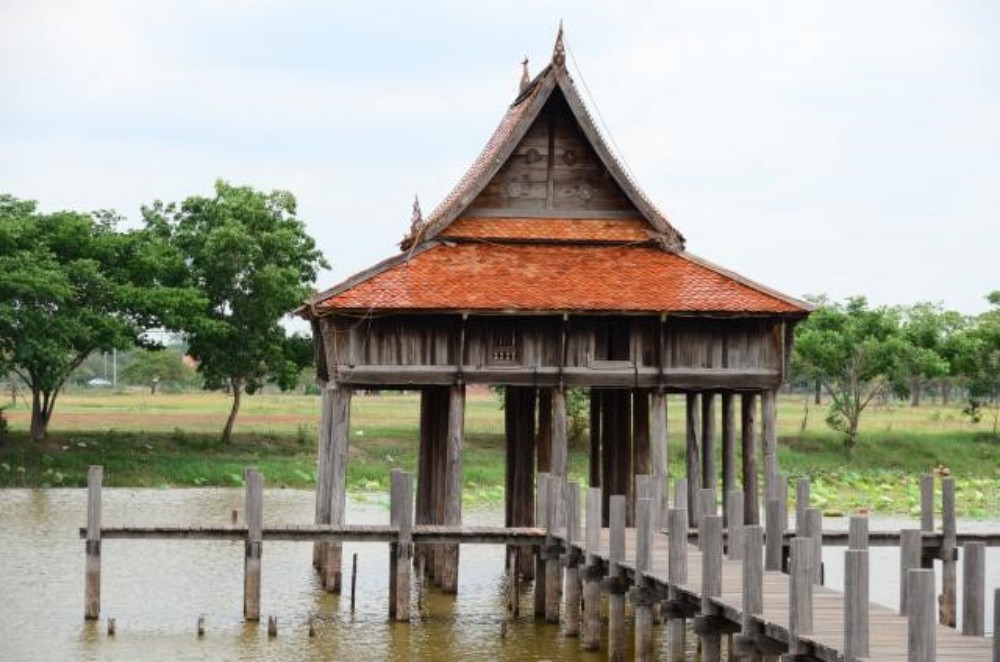
5. Design of a building in the middle of the water and water casting or oil surrounding the building to prevent termite access However, building maintenance must be considered. Including the addition of later buildings such as the water tower of various temples Maruekhathaiyawan Palace Wat Pa Rattanawan, etc.

. Source: Faculty of Architecture. Prince of Songkla University.
Research project to manage knowledge of housing and way of living through local wisdom in the southern region, 2013.
6. Elevating the building floor from the ground level raising the basement and a monolithic or concrete base in order to easily observe the walking paths of termites, such as southern vernacular architecture
. Source: https://www.researchgate.net
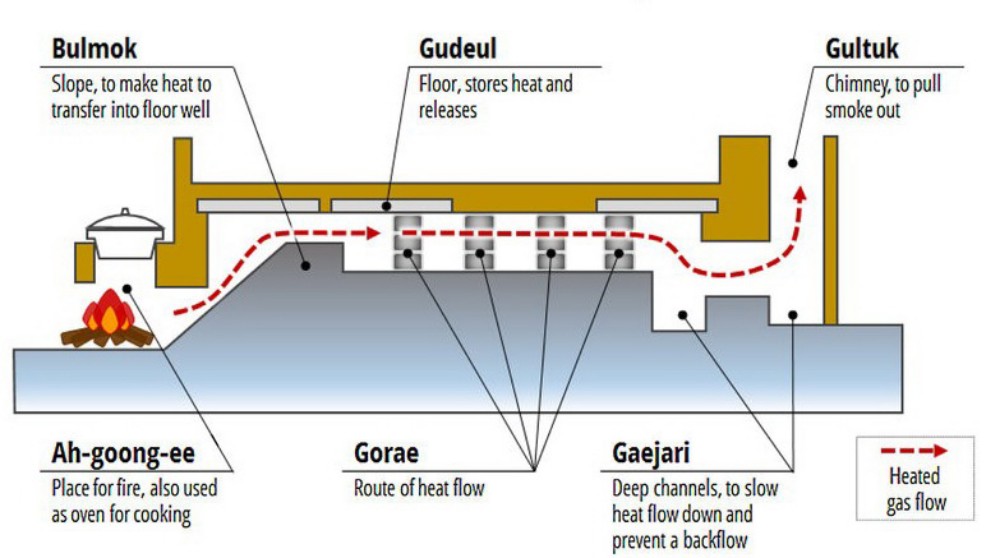
7. The design of the floor heating system of buildings in cold countries. besides the warmth There are also by-products of heat vapor and soot that can help drive insects and termites out of the building, such as the Ondol floor heating system of Korea.

Summary of termite prevention guidelines without creating toxins
1. Design and manage the environment To reduce the factors of termite nesting, including
- Elimination of food sources under and around the building such as tree stumps, wood chips, cement bags
- eliminating food sources inside the building by choosing a wood substitute material or materials that are resistant to termites
- Controlling humidity inside the building and around the building, for example, designing a raised platform to ventilate the humidity under the building.
- Design to reduce building blind spots This may be the access path of underground termites. To be able to clearly observe the walking paths of termites and be able to solve problems immediately
- plant design by determining the location of planting large trees away from the building to prevent the access of termites from the tree canopy

Source: http://apcsydney.com.au/2015/07/30/how-do-termites-get-into-your-home/
2. Design and installation of physical termite protection system to create a barrier to obstruct the access of termites With forms such as gravel, crushed stone, salt, water, oil, sheet metal, metal grating or plastic sheeting, etc., in every joint of the structure that may be a termite access route to the building.
3. Regular inspection of buildings and surveying the walking paths of termites. both by observing and the use of detectors for heat, humidity, gas, frequency or sound waves. to prevent damage that may occur.
reference list
Jarunee Wongkaluang. Advisor to the Royal Forest Department. Interview, 21 May 2018.
Jarunee Wongkhaluang and Yupaporn Soranuwat. General knowledge about termites. and prevention and elimination. Bangkok: Bureau of Forest Economics and Product Research, Royal Forest Department, 2001.
Charunee Vongkaluang. Current Termite Management in Thailand. Proceedings of the 1st Conference of the Pacific-Rim Termite Research Group (Malaysia), March 2004.
Dong-heub Lee. Current Termite Management in Korea. Proceedings of the 1st Conference of the Pacific-Rim Termite Research Group (Malaysia), March 2004.
James W. Creffield and Michael Lenz. Current Termite Management in Australia. Proceedings of the 1st Conference of the Pacific-Rim Termite Research Group (Malaysia), March 2004.
Kunio Tsunoda and Tsuyoshi Yoshimura. Current Termite Management in Japan. Proceedings of the 1st Conference of the Pacific-Rim Termite Research Group (Malaysia), March 2004.
Kunio Tsunoda. Improved Management of Termites to Protect Japanese Homes. Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Urban Pests (Singapore), January 2005.
The Research & Innovation for Sustainability Center (RISC) is Asia’s first innovation-focused research and development center for quality of life. It consists of a network of researchers, innovators, experts, as well as manufacturers. To create a variety of innovations that can be extended to improve the quality of life and health of all living things in the world (For All Well-being), including restoring and maintaining the environment in balance. Conducive to the life of all things with happiness, quality and sustainability.
Follow FB : riscwellbeing
Subject : Research and Innovation Center for Sustainability
Arranged by: Sarayut Srithip-art




